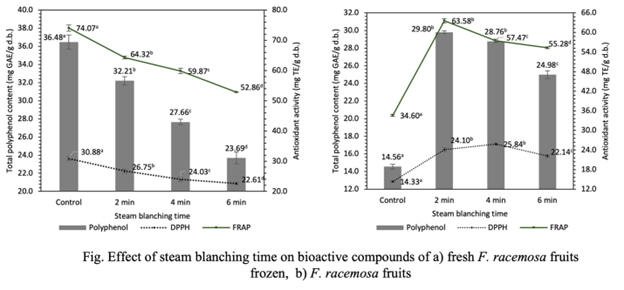
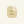Ficus racemosa (L.) belongs to the Moraceae family, this plant has been shown to have an abundant source of phytochemicals and health benefits. It is often used as a traditional medicine to support the treatment of various diseases, and it is also used as food in some countries. The study was aimed to evaluate the influence of the pretreatment method on the biological activity of F. racemosa (L.) dried fruits. Fresh fruits have been sliced, soaked in citric acid 1% (w/v) for 20 min, and blanching or blanching and freezing treatment. The blanching method, including steam blanching and hot water blanching, was investigated with blanching time as a factor. The blanching and freezing method, blanching parameters were evaluated with time or temperature blanching as a factor. The one-factor-at-a-time or temperature was used to design the experiment in which four-level. After each pretreatment condition, the sample was dried by convection at 60 °C until the moisture content was 0.05 g/g of sample on the dry basis (d.b). Then, the dried sample was analyzed to determine the total phenolic content, antioxidant capacity by DPPH radical scavenging assay and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay. The findings indicated that blanching is not conducive to maintaining the antioxidant activity of F. racemosa fruits. In the case of blanching and freezing before drying, blanching with steam for 2 min or blanching with water at 80 oC for 2 min improves the antioxidant activity of the product by about 1.6 to 2 times.